REFINER: Reasoning Feedback on Intermediate Representations
February 4, 2024 | 436 words | 3min read
Paper Title: REFINER: Reasoning Feedback on Intermediate Representations
Link to Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.01904
Date: 4. April 2023
Paper Type: LLM, prompting
Short Abstract:
LLMs have demonstrated remarkable performance on reasoning tasks. In this paper, the authors introduce REFINER, a framework for fine-tuning LLMs to generate explicit reasoning steps.
1. Introduction
Numerous papers have highlighted the importance of generating explicit reasoning steps for improving a model’s performance and interpretability. However, these steps can be unreliable or incorrect. Typically, the approach to solve this, involves annotating new data with fixed errors and fine-tuning the model on this data, a process that demands significant computational resources and time.
REFINER employs iterative specific feedback to refine the reasoning of the LLM. This is accomplished through two models: a generator that produces text and a critic that provides feedback on the intermediate reasoning steps for the generator.
The Critic model is trained on a dataset consisting of reasoning errors and structured feedback on these errors, which is automatically constructed. The critic model provides feedback to the generator model during both training and inference.
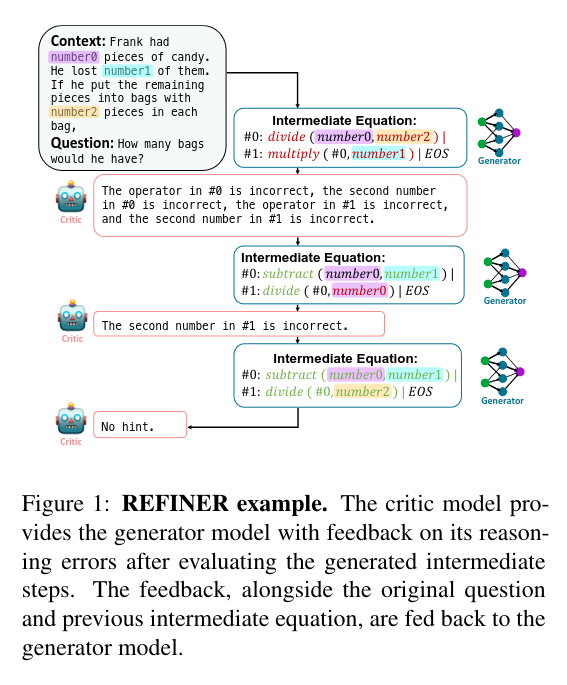
2. REFINER
The authors of the paper use the following benchmarks to test the model’s ability:
- Synthetic natural language reasoning(sNLR): Given a Scenario and some synthetic rules, the models needs to deduce some fact.
- Math word problem (MWP): Given a word problem consisitng of a context and a question, the goal is to map the problem to a mathematical expression.
- Moral norm and action generation for moral stories (MS): Given a situation, an intention, and an immoral action. The model needs to generate the moral action.
To solve these benchmarks, the authors force the model to generate intermediate reasoning steps using two different models:
- Critic: Which generated verbal structured feedback to the intermediate reasoning steps.
- Generator: Which generates the intermediate reasoning steps.
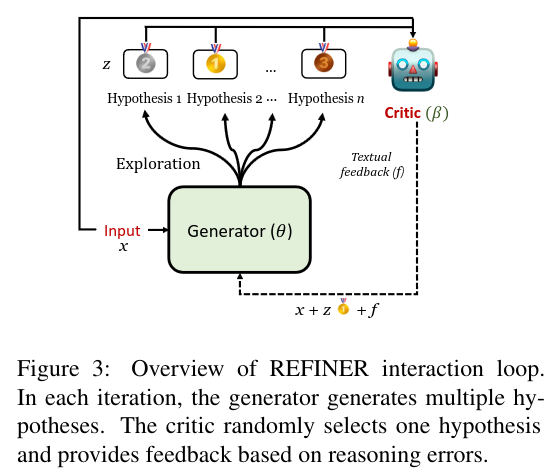
2.1 Critic Model
To train the critic models, pairs of reasoning steps and structured feedback are needed. The model is then trained in a supervised setting using cross-entropy loss.
2.2 Generator Model
The generator is trained given a context to generate plausible reasoning steps. At each iteration, the generator produces multiple possible reasoning steps. The critic randomly selects one reasoning step and provides feedback on it, ensuring exploration of the action space. The generator is updated using cross-entropy loss.
3. Results
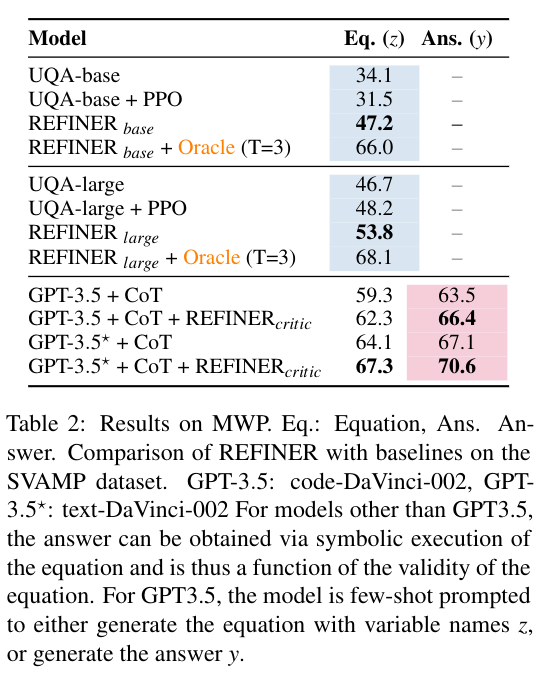
The authors observe that REFINER can significantly improve the model’s performance. Additionally, optimal feedback from the critic results in even stronger performance for REFINER.
4. Conclusion
This paper introduces the REFINER framework to enhance the reasoning abilities of LLMs through an iterative feedback loop between two models. The evaluation conducted by the authors demonstrates promising results.