SWE-agent: Agent-Computer Interfaces Enable Automated Software Engineering
May 30, 2024 | 777 words | 4min read
Paper Title: SWE-agent: Agent-Computer Interfaces Enable Automated Software Engineering
Link to Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.15793
Date: 6. May 2024
Paper Type: LLM, Agents, Software-Engineering
Short Abstract:
This paper introduces SWE-agent, which is an autonomous system that uses LLM to fix real life GitHub issues. The Agent is tested on SWE-Benchmark and achieves a success rate of 12.5%.
1. Introduction
In recent times, LLMs have become very popular tools in software development, mostly to generate small snippets of code and auto completion. In these cases the human serves as mediator between the problem and the LLM. For instance providing error messages to refine the code. In this paper, the authors introduce SWE-Agent which is an autonomous system, bases on a LLMN, that solves real world Software-Engineering problems. For that it outputs thoughts and actions(ReAct) and receives feedback from the environment based on it.
The main part of the paper, is designing an agent-computer interface(ACI), which they find outperforms existing interfaces such as the Linux Shell. The Linux-shell is not a good environment for agents, for example:
- does not provide simple commands to edit small chunks of files
- does not provide good feedback when invalid edits are made
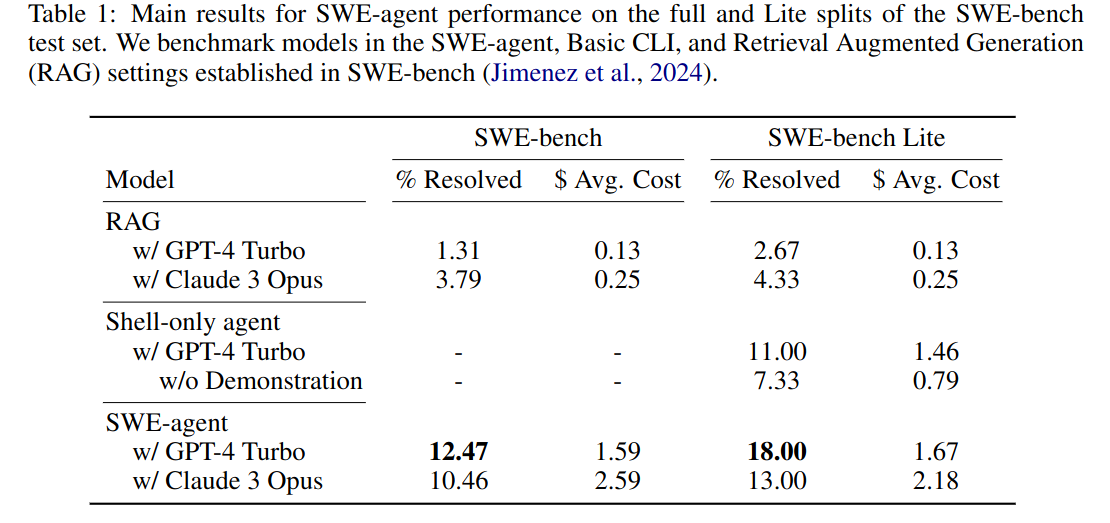
They show when using GPT-4 Turbo that tehy have a sucess rate of 12.5% on the SWE benchmark, beating the previous SOTA of 3.8% which uses RAG system. Also, they find using their ACI the model solves 10.7% more issues than when using the Linux Shell.
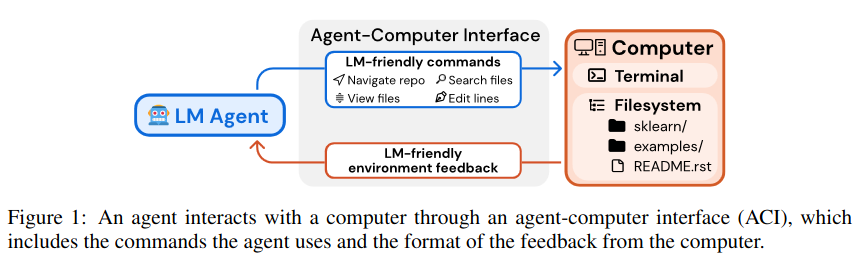
2. The Agent-Computer Interface
The System is an Agent, because the LLM interacts with the environment through action and receives feedback. In this system, the environment is entirely digital consisting of the GitHub repository of which the system should solve issues.
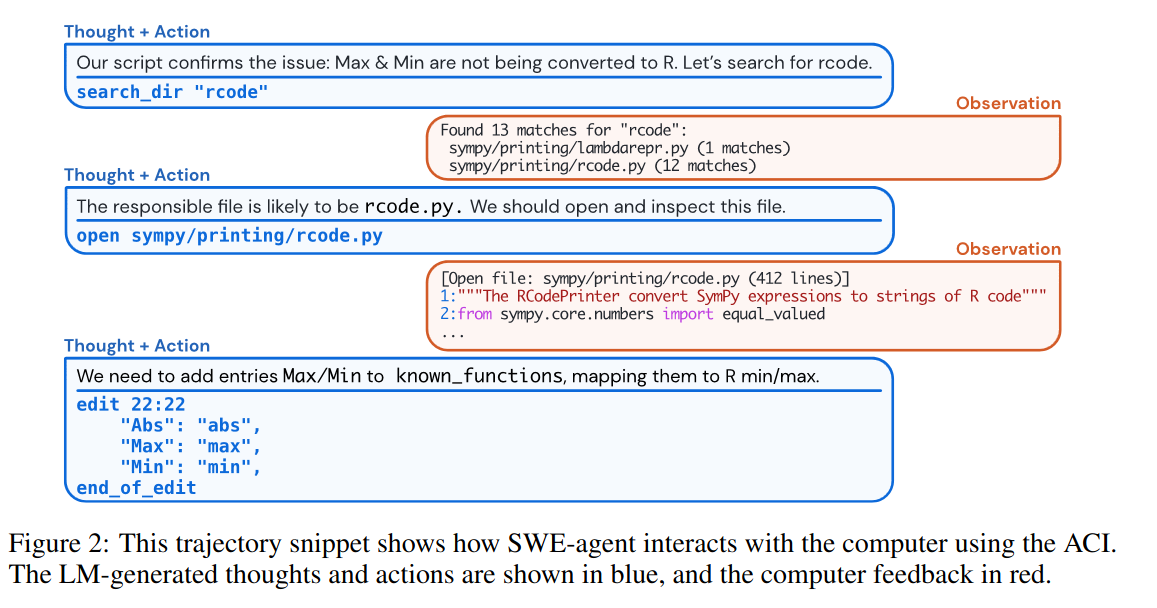
The Agents switches between issuing command and the computer responding with feedback. The ACI specifies the available commands. Through observations they find that the following points make for an effective ACI:
- Action should be simple and easy to understand, i.e. bash commands often have many options which makes usage complicated.
- Action should be efficient, i.e. file navigation and efiting should use as few actions as possible.
- Environment feedback should be informative.
- Guardrails mitigate error propagation, LLMs often struggle to recover from errors.
3. Designing the ACI
Existing application interfaces have been designed with humans in mind e.g. vscode, vimbut may not be suited for LLMs. Furthermore humans can ignore unexpected input such as accidently outputting a binary file with tousands of lines, LLMs can’t. Commands that suceed silently confude the LLM, because it doesn’t get any feedback. LLMs will often expend extra action to verify the sucess of operations.
To address these challanges, SWE-Agent introduces an ACI tailored towards LLMs. A well designed ACI should help the agent to recover from misstakes, understand the current state of the repository and supress any unusual lengthy programs outputs.
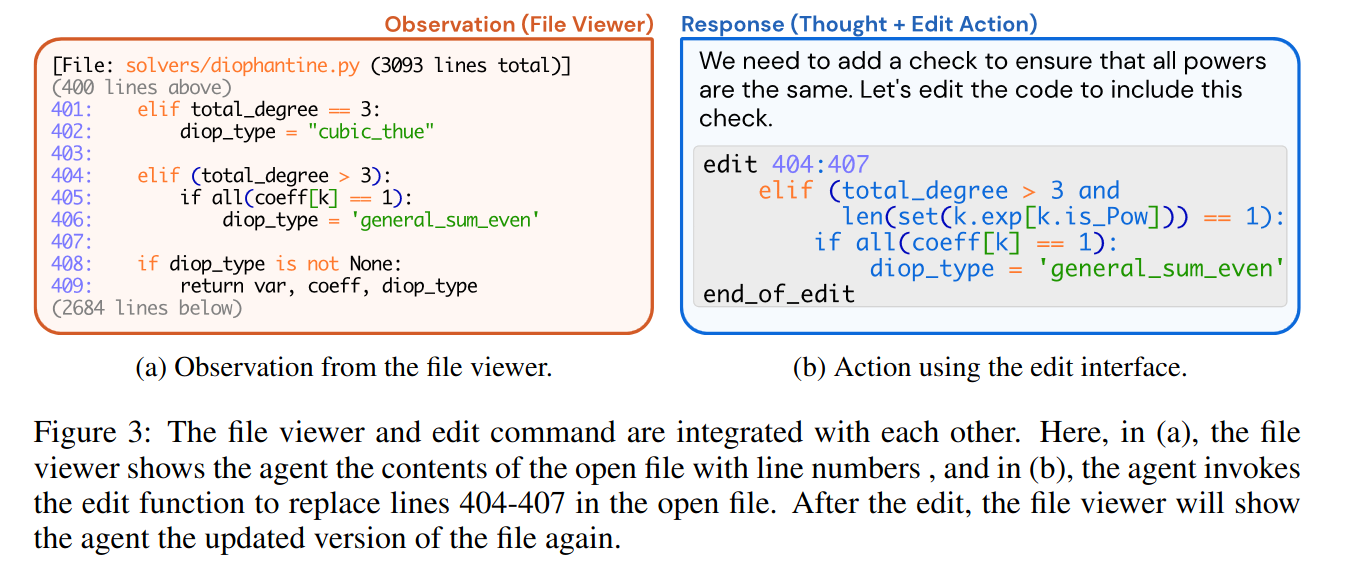
The ACI is built on top of the linux shell and allows for the following actions:
- search/navigation, e.g.
find_file,search_file,search_dir. - file viewer, presents a window of at most 100 lines, the agent cant move the window through the commands
scroll_down,scroll_up. - file editor, the
editcommand takes three arguments: start line, end line, and the replacement text. After edits are applied, the file viewer displays the updates content. - context managment, it uses informative-prompts, error messages and history to keep information.
4. Experimental Setup
Dataset
The SWE-Agent is evaluated on the SWE-Benchmark which consists of 2,294 tasks from different popular python repositories.
Model
They use GPT-4 Turbo, Claude 3 and Llama 3. Many context windows of LLMs are too small e.g. llama3.
Baseline
They compare the SWE-Agent against non-interactive RAGs.
5. Results
SWE-agent with GPT-4 Turbo yields the best performance, solving 12.47% of the SWE-benchmark.
5.1 Analysis of ACI
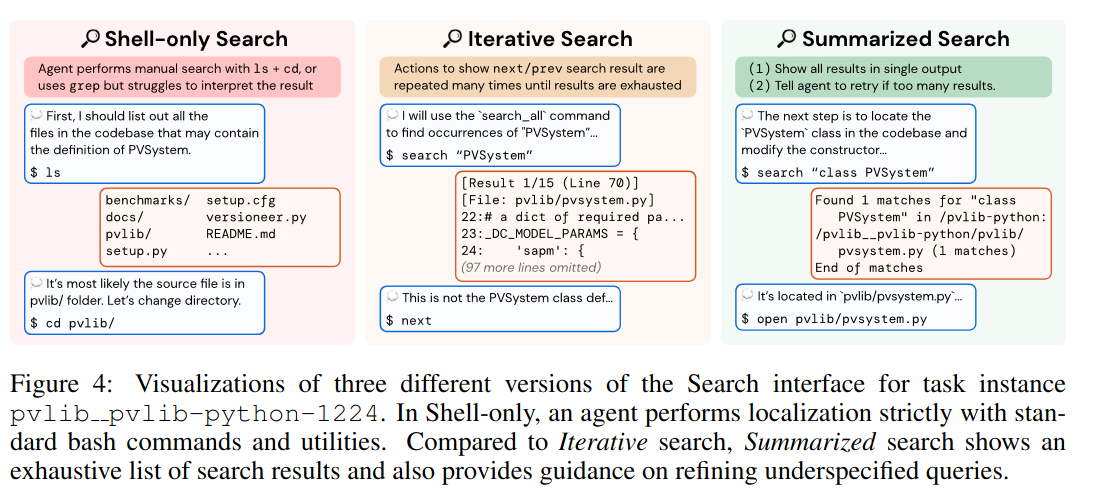
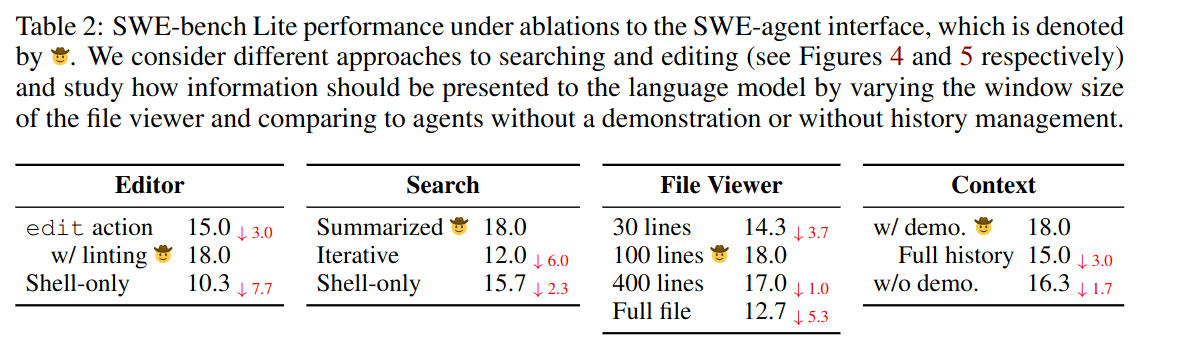
When given a large number of search results, the agents tends to looks through each one, which isn’t great. This inefficient behaviour can lead to worse performance than shell only setting(15.7% for shell only vs 12.0% for iterative search).
Agents are sensitive to the number of lines shown in the editor, too few lines(30 lines, 14.3%) or too many lines(entire file, 12.7%). Using linting for the file viewer also improves the performance.
5.2 Analysis of Agent Behaviour
Interesting model behaviour:
- SWE-agents usually start the problem by attempting to reproduce the issue
- From turn 5 on the most frequent actions are
editandpython - Runs that are submitted with few steps are more liekly to suceed than runs with a large number of steps.
6. Discussion
The authors introduced SWE-Agent an autonomous agent that aims to solve software develoment issues. For that they designed their own agent-computer-interface(aci) which they tailroed to LLMs, which was the leading cause for the sucess of SWE-Agent.