Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback
February 5, 2024 | 535 words | 3min read
Paper Title: Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback
Link to Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02155
Date: 4. March 2022
Paper Type: NLP, LLM, Instruction, Alignment
Short Abstract:
This paper introduces a novel technique, instruction fine-tuning, to enhance the alignment of Language Models (LLM) with user instructions. The approach utilizes reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) and demonstrates its effectiveness by applying it to GPT-3.
1. Introduction
Language Models (LLM) can be prompted for natural language tasks, but often, the results deviate from the given instructions. This misalignment occurs because LLMs are trained to predict the next token in their input rather than to follow specific tasks. To address this issue, the authors propose instruction fine-tuning, employing reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to better align the model’s objective with the intended task. This technique utilizes human preferences as a reward signal to fine-tune the models.
To implement this, the authors train a reward model (RM) predicting the reward a human would give for a given LLM prompt and its output. The dataset includes manually labeled prompts, GPT-3 outputs, and human-written demonstrations. The RM is then used as a reward function to fine-tune the base model using the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm.
The study reveals a significant preference for InstructGPT outputs over GPT-3 outputs, indicating that fine-tuning LLM with human preferences improves performance across various tasks.
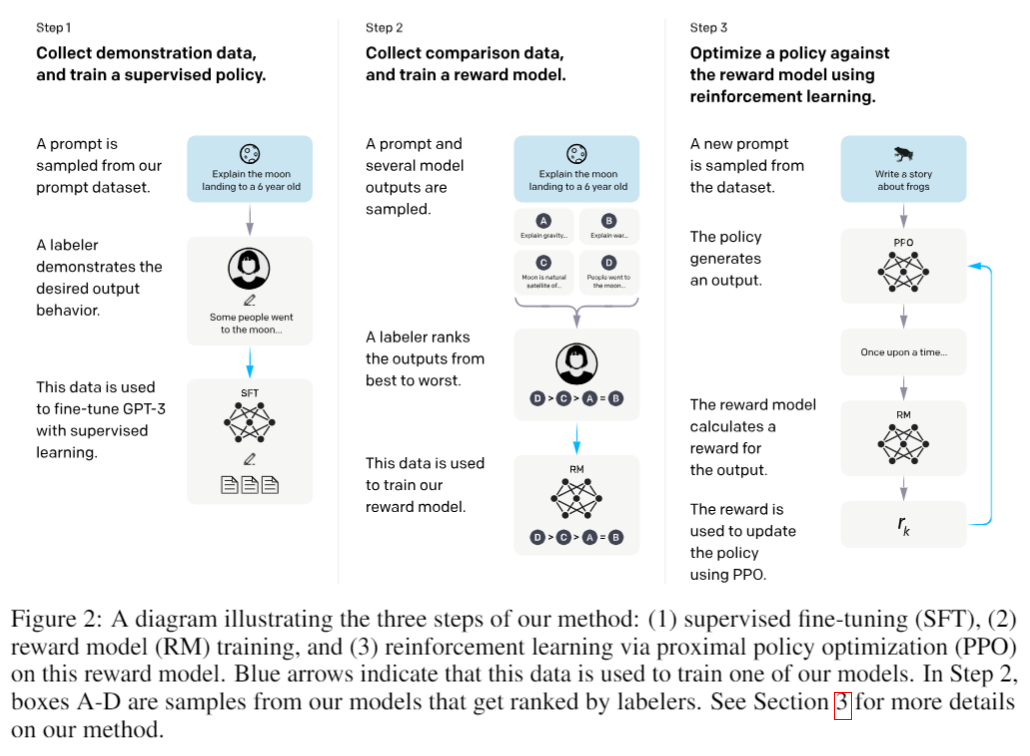
2. Method
They start with an already pretrained LLM and a dataset on which they want to align the LLM. After which they do the following three steps:
- Collect demonstration data, and train a supervised policy: labellers provide demonstrations of the desired behaviour on the input prompts.
- Collect comparison data, and train a reward model: dataset of comparisons between model outputs, where labellers indicate which output they prefer for a given input, the RM is trained to predict the human reward.
- Optimize a policy against the reward model using PPO: for that they use the output of the RM as reward and fine-tune using the PPO algorithm. Steps 2. and 3. can be repeated until the desired performance is reached.
2.1 Data
The dataset consists of text prompts submitted to OpenAI API, with all Personally Identifiable Information (PII) removed. Three types of prompts were used:
- Plain: they asked the labellers to come up with an arbitrary task.
- Few-shot: the labellers should come up with an instruction, and multiple query/response pairs for that instruction.
- User-based: the labelers should come up with a prompt based on specific use-cases.
2.2 Models
All models started with the pre-trained LLM GPT-3 as the baseline. Different training techniques were applied:
- Supervised fine tuning(SFT): Utilizing dropout and learning rate decay.
- Reward Modelling(RM): Starting from the SFT model and removing the final embedding layer, they trained the RM with a size of 6B.
- Reinforcement Learning(RL): Using the RM to fine-tune an SFT model using the PPO algorithm.
3. Results
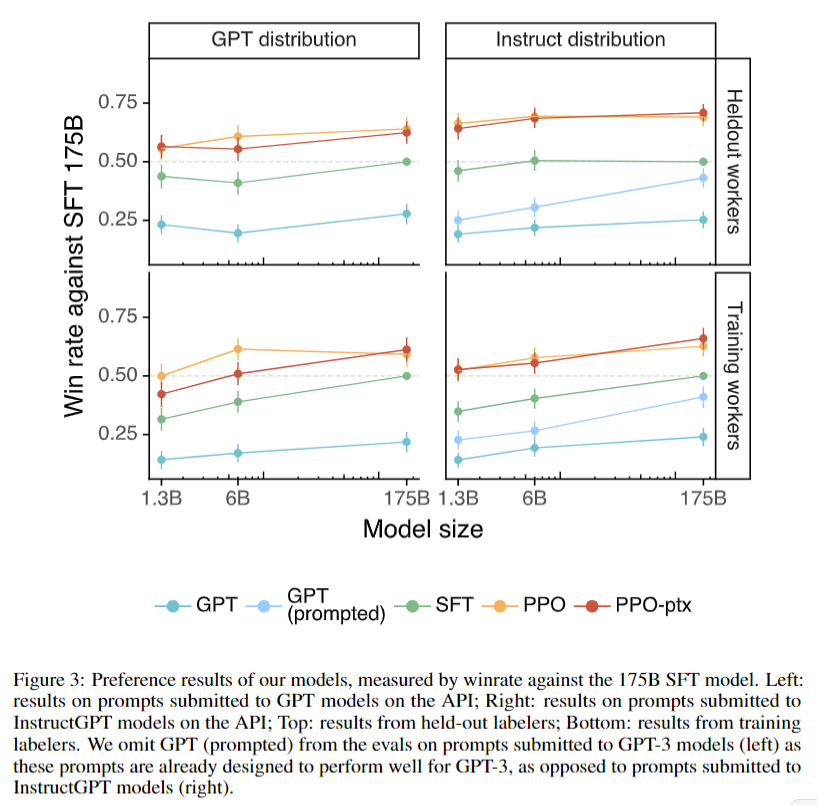
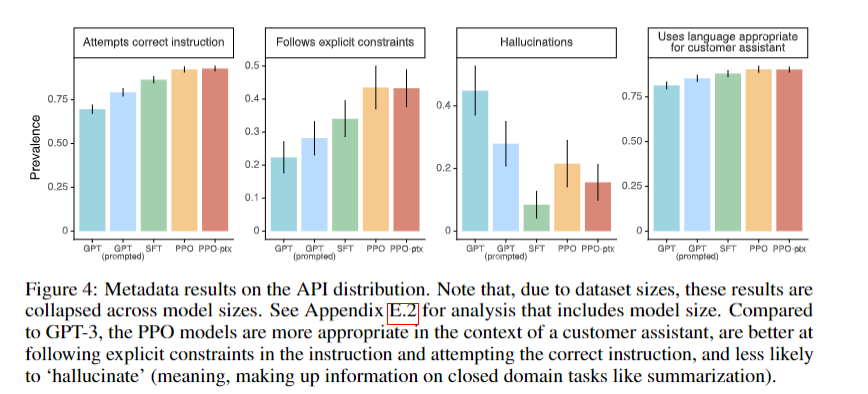
Labelers significantly preferred InstructGPT outputs over GPT-3 outputs. An “alignment tax” issue with the default PPO algorithm was addressed by using the PPO-ptx algorithm.
4. Conclusion
This paper demonstrates the effectiveness of instruction fine-tuning for improving the alignment of models with user instructions. The proposed technique is now considered an industry standard for chatbots and other LLM agents.